6H30.10 – Polarizers
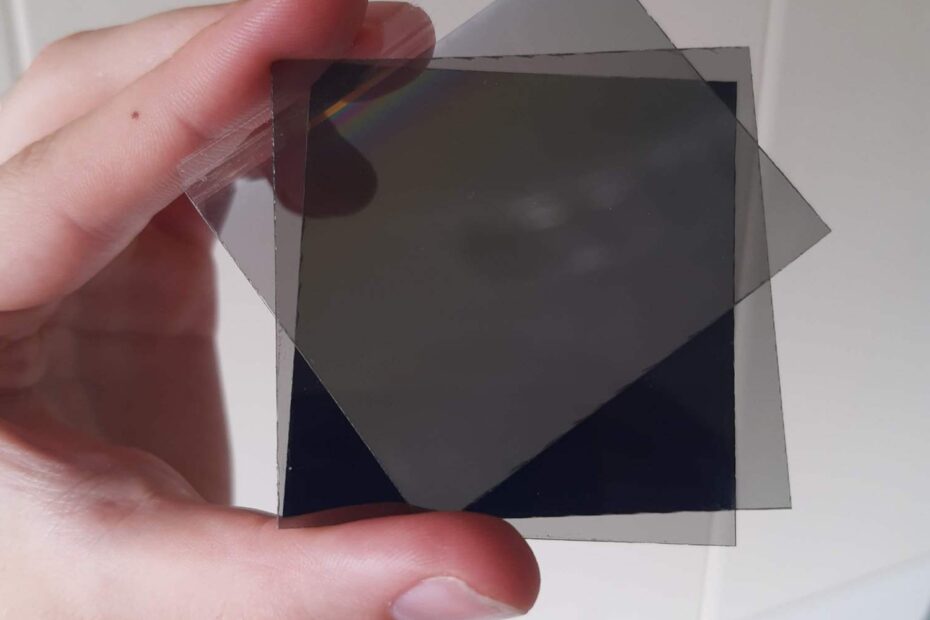
The two polarizer setup filters vertically and horizontally, so no light gets through. By adding a third one one in between, a superposition of vertical and horizontal polarization is induced in the light from the first polarizer, thus some light can pass through the third one. Also known as the Dirac three polarizer experiment